We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more
The Difference Between Prebiotics, Probiotics and Postbiotics for Horses
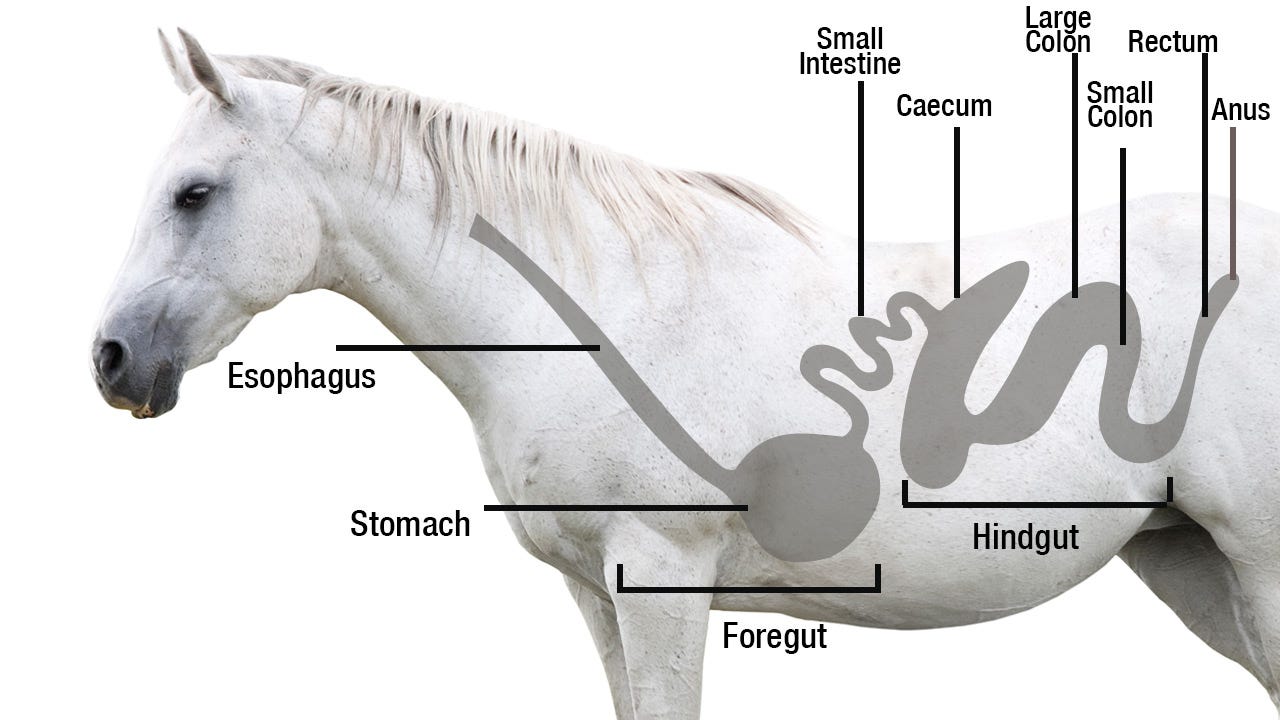
Prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics for horses are all related to the concept of maintaining a healthy gut microbiota, but they have different roles and functions.
Here's a breakdown of each term:
Prebiotics for horses
Prebiotics for horses are non-digestible fibers or compounds that serve as a food source for beneficial bacteria in the horse's gastrointestinal tract. These prebiotics promote the growth and activity of specific types of bacteria in the horse's gut, such as fiber-fermenting bacteria.
Prebiotics commonly used for horses include substances like fructooligosaccharides (FOS), inulin, and certain types of fibers.
By nourishing the beneficial bacteria in the horse's gut, prebiotics can help improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and support overall gastrointestinal health in horses.
Probiotics for horses
Probiotics for horses are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, provide health benefits to the horse.
These microorganisms can be bacteria or yeast strains that are similar to the beneficial bacteria naturally present in the horse's gastrointestinal tract.
Probiotics for horses are typically administered orally and can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota, support digestion, improve nutrient utilization, and potentially alleviate digestive issues in horses.
Common probiotics used for horses include strains of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and saccharomyces.
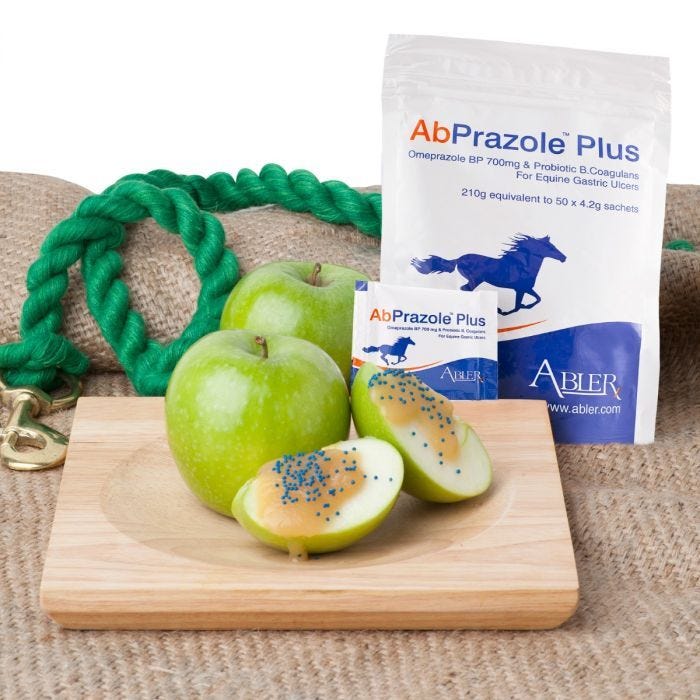
Abler's AbActive is a probiotic developed to assist in restoration of natural intestinal flora, which can lead to a more rapid recovery and better nutrient absorption. Priced from just $0.65c per serve, each 3g sachet of enteric-coated granules contains 45 billion cfu probiotic B. coagulans (lactobacillus sporogenes).
Visit the AbActive Shop Page here for more information.
Postbiotics for horses
The concept of postbiotics for horses is relatively new, and research is ongoing.
Postbiotics for horses refer to the metabolic byproducts or substances produced by probiotic bacteria during their fermentation process in the horse's gut.
These byproducts include short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate, as well as other bioactive compounds. Postbiotics can have direct positive effects on the horse's gut health, including promoting a healthy gut lining, supporting the immune system, and potentially reducing inflammation.
However, further research is needed to fully understand the specific benefits and applications of postbiotics for horses.
Summary
In summary, prebiotics for horses are non-digestible fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, probiotics for horses are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, and postbiotics for horses are the byproducts produced by probiotic bacteria during fermentation that may have direct positive effects on gut health. These concepts are important for maintaining a healthy gut microbiota and promoting overall digestive health in horses.






Validate your login